Wolf Spider vs Tarantula Top 5 Differences
Ever found yourself face-to-face with a hairy, multi-legged creature and wondered, “Is that a wolf spider or a tarantula?” These two arachnids often get mistaken for each other due to their similar appearance and the fact that they both belong to the spider family. However, despite their shared traits, significant differences set them apart. This article delves into the top 5 key distinctions between wolf spiders and tarantulas, helping you to identify them with confidence. From their physical attributes to their behaviors, we’ll explore what makes each of these fascinating creatures unique. Knowing the differences can be vital, especially if you’re trying to determine whether a spider poses a threat or simply prefers to be left alone. Let’s embark on a journey to understand these amazing arachnids!
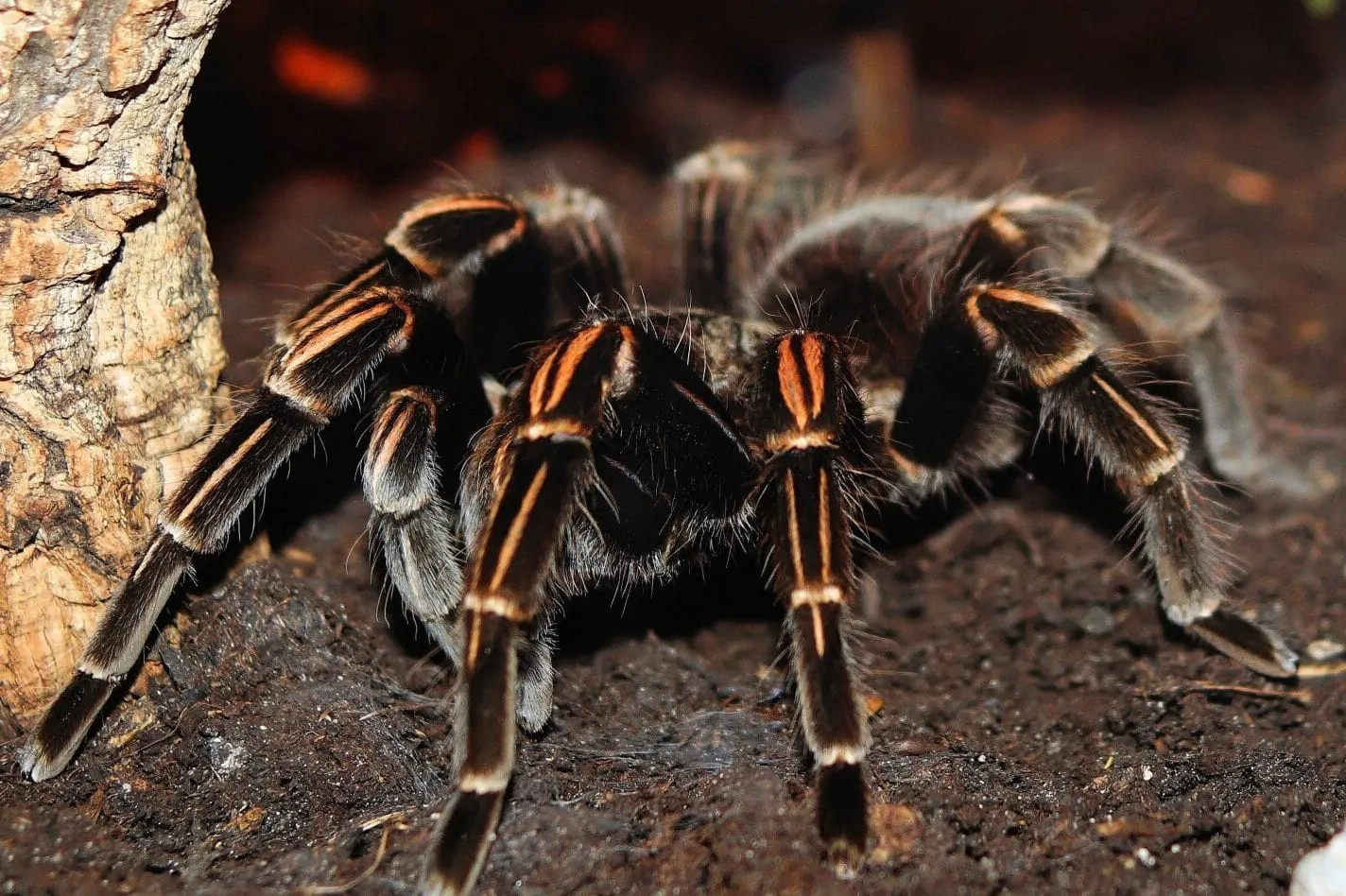
Size & Appearance
Size is often one of the most noticeable differences when distinguishing between a wolf spider and a tarantula. Tarantulas, in general, tend to be larger than wolf spiders. While individual sizes can vary depending on the species and age of the spider, tarantulas typically have a significantly larger leg span and overall body mass. The hairy appearance of both can be intimidating, but the extent and distribution of this hair, along with other physical characteristics, offer clues to their identity.
Body Features Differences
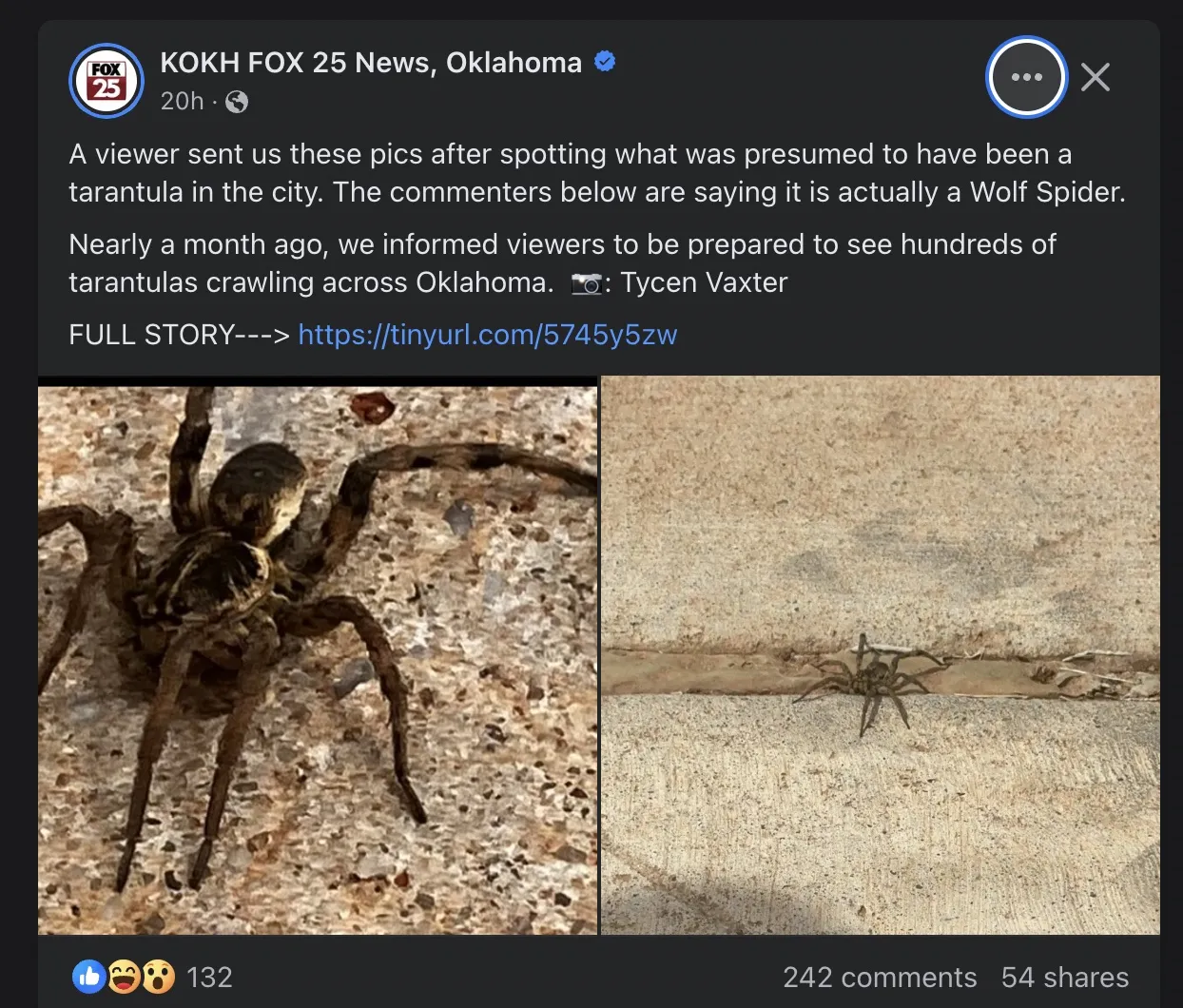
One of the primary distinctions in appearance lies in their body features. Wolf spiders have a body that is generally more elongated, and their coloration varies, often featuring shades of brown, gray, and black, with patterns that provide camouflage. They possess a distinct eye arrangement that helps them to hunt. Tarantulas, on the other hand, are usually more bulky, with a rounder abdomen. Their coloration is incredibly diverse, ranging from browns and blacks to vibrant blues, oranges, and reds, depending on the species and its environment. The hairs on tarantulas are also different; they often have urticating hairs that they can flick off as a defense mechanism, whereas wolf spiders do not have this. Both spiders have eight legs, but the overall look and feel differ significantly.
Leg Span Differences
Leg span is a straightforward way to gauge whether you’re looking at a wolf spider or a tarantula. As mentioned previously, tarantulas generally boast a larger leg span, often reaching up to 12 inches or more in some species. This wide stance allows them to cover more ground and appear more imposing. Wolf spiders, while also having a respectable leg span, typically range from 1 to 4 inches depending on the species. Comparing the leg span is a quick visual check to differentiate between the two types of spiders. If you see a very large spider, chances are it is a tarantula (see image wolf-spider-size.webp and tarantula-size.webp).
Habitat & Geographic Distribution
Where you find these spiders can also provide clues to their identity. The habitats and geographical distributions of wolf spiders and tarantulas differ significantly. Understanding where they live can help you predict which spider you might encounter in a given area.
Where Wolf Spiders Live
Wolf spiders are incredibly adaptable and can be found in a wide variety of habitats. They are present in almost all parts of the world, from grasslands and forests to gardens and even your own backyard. These spiders are often seen scurrying along the ground or hiding under rocks, logs, or leaves. Wolf spiders are skilled hunters and will often be seen on the prowl, actively seeking prey. Because they are not web builders, they must be fast and efficient predators to survive. They also tend to prefer more temperate climates, though some species have adapted to cooler regions. (see image wolf-spider-habitat.webp).
Where Tarantulas Live
Tarantulas, on the other hand, have a more limited geographical distribution. They are typically found in warmer regions, including the southwestern United States, Central and South America, and various parts of Asia, Africa, and Australia. Their preferred habitats are often arid or semi-arid environments, such as deserts, grasslands, and tropical forests. Tarantulas are burrowing spiders, though some species live in trees. They often create elaborate burrows in the ground, lined with silk, or they take shelter under rocks or in crevices. Their habitat preferences make them less likely to be encountered in colder climates. (see image tarantula-habitat.webp)
Venom & Bite
While both wolf spiders and tarantulas are venomous, the potency and effect of their venom differ. It is essential to understand the potential impact of a bite from either type of spider. While they are venomous, the danger they pose to humans is often overstated.
Wolf Spider Venom

Wolf spider bites are generally considered to be less dangerous than tarantula bites. Their venom is not considered medically significant, but a bite can still be painful. The bite may cause localized pain, redness, and swelling, similar to a bee sting. Rarely, some individuals may experience allergic reactions. Wolf spiders are not aggressive and will only bite if they feel threatened or are provoked. Their primary defense mechanism is speed and evasion.
Tarantula Venom
Tarantula bites can also be painful, and the effects can be similar to those of a wolf spider bite. However, tarantula venom is generally considered to be mild to humans. The bite itself, caused by the large fangs, can be more physically damaging than the venom itself. Some tarantulas also have urticating hairs on their abdomen that can be flicked at a perceived threat, causing skin irritation and itching. While not typically life-threatening, a tarantula bite can cause localized pain, redness, and itching. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience severe symptoms or an allergic reaction.
Hunting & Feeding Habits
Both wolf spiders and tarantulas are predators, but their hunting and feeding habits differ based on their environment and physical capabilities. Observing how they hunt gives insight into their survival strategies.
Wolf Spider Hunting Tactics

Wolf spiders are active hunters, meaning they actively seek out their prey rather than waiting in webs for it to come to them. They possess excellent eyesight and use it to spot potential meals, such as insects, other spiders, and even small vertebrates. They are fast runners, which helps them chase down prey and quickly escape threats. Because they do not build webs, they rely on their agility, speed, and hunting prowess to secure their meals. (see image wolf-spider-hunting.webp)
Tarantula Hunting Tactics
Tarantulas typically ambush predators, although some species do actively hunt. Many tarantulas wait in or near their burrows for prey to wander by. When a meal gets close enough, they quickly pounce and use their fangs to inject venom. Their diet mainly consists of insects, but larger tarantulas can take down small lizards, frogs, and even small mammals. They are patient hunters, relying on their size and strength to overpower their prey. (see image tarantula-hunting.webp)
Behavior & Temperament
The behavior and temperament of wolf spiders and tarantulas vary. Understanding their typical reactions can help you predict their behavior in encounters and better appreciate these creatures.
Wolf Spider Behavior

Wolf spiders are generally shy and non-aggressive. They prefer to avoid confrontation and will usually run away if they feel threatened. They are solitary creatures and tend to live and hunt alone, except during mating season. Females are known for carrying their egg sacs attached to their spinnerets and, after the spiderlings hatch, carrying them on their backs. Their primary goal is to survive by hunting and avoiding threats. They pose little threat to humans and are considered beneficial in controlling insect populations.
Tarantula Behavior
Tarantulas also are generally not aggressive. However, they can be defensive if they feel threatened. They may display warning behaviors, such as rearing up on their hind legs, before biting. The urticating hairs on some species serve as a primary defense mechanism. Tarantulas are solitary creatures, except during mating season. They tend to be more secretive, spending much of their time in burrows or hiding spots. When kept as pets, they can be surprisingly docile, but it is important to handle them with care and respect. Tarantulas, like wolf spiders, play a crucial role in their ecosystem by controlling insect populations.
In conclusion, while wolf spiders and tarantulas share some superficial similarities, they are distinct creatures. From their size and appearance to their habitats, venom, and behaviors, understanding the differences helps you identify them. By knowing what to look for, you can identify the spider and admire these fascinating arachnids from a safe distance.
